September 30, 2024
What is a telephoto lens? Introducing key tips on how to use a telephoto and how to choose the right lens
What is a telephoto lens? Introducing key tips on how to use a telephoto and how to choose the right lens
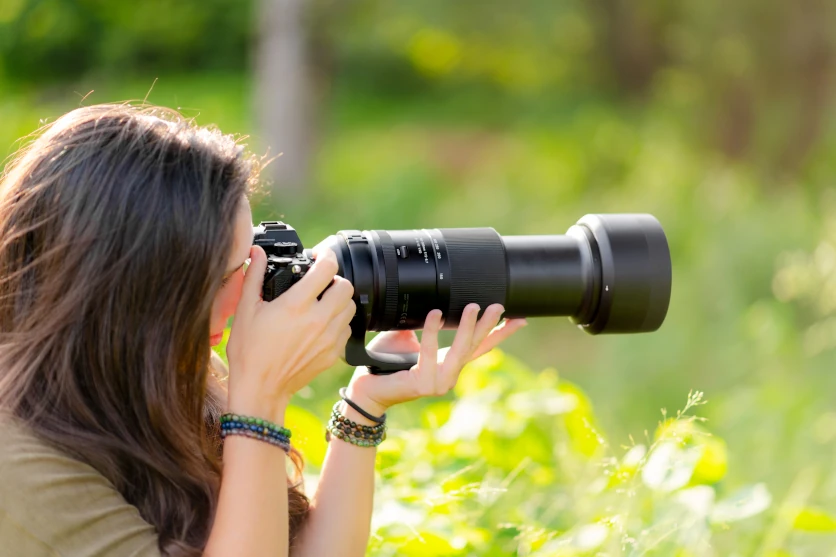


A telephoto lens allows you to enlarge a distant subject can capture it in fine detail. Telephotos are used in various situations such as shooting sports, wild birds, animals and railway photography. On the other hand, when it comes to this genre of photography, some people may have the impression that telephotos are the exclusive domain of professional photographers who excel in their use. But telephotos are also used in many day-to-day situations such as portraits, landscape photography, and children’s sports days and recitals. That’s why in this article we will talk about the different characteristics and types of telephoto lens, explain what situations are best suited to the use of a telephoto, and share some tips on how to choose one.
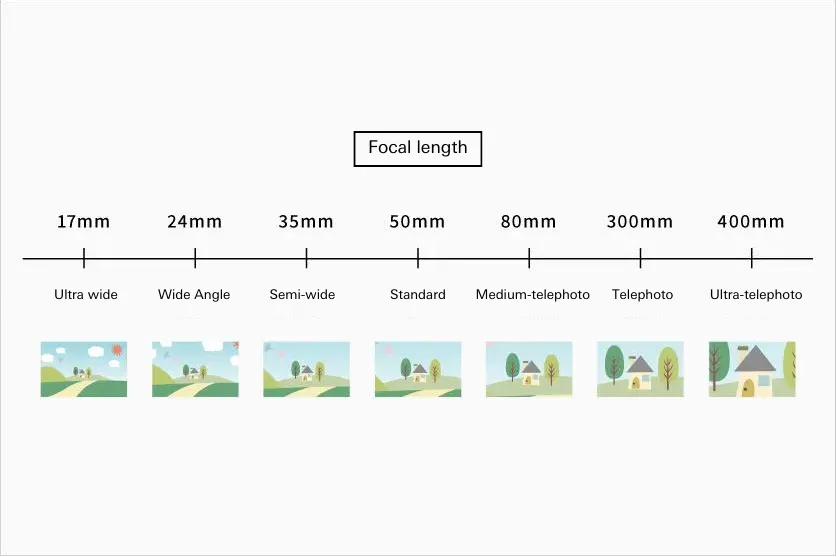
Generally, a lens with a focal length of around 80mm or greater is referred to as a telephoto lens. Characteristically, a telephoto lens has a narrow angle of view and enlarges distant subjects. As a telephoto lens has a shallow depth of field making it easier to produce bokeh in the background, it allows you to take photos where the central subject stands out.
Now let’s explore the characteristics of telephoto lenses in more detail.
As mentioned above, the first characteristic of a telephoto lens is that it allows you to render an enlarged view of distant subjects. Compared with a standard lens, for example, a telephoto lens has a narrower angle of view and there is less information captured in the background. For that reason, a telephoto lens lets you isolate your subject or some other object you wish to photography and express it as the main subject.
A telephoto lens also lets you clearly capture fine textures and detailed elements of a subject even when you cannot physically get close, such as when photographing skittish animals.
The second characteristic of a telephoto lens is compression effect. Compression effect is an effect that makes distant objects appear closer together, thereby “compressing” the sense of distance. For example, even when capturing a scene of buildings that are essentially equally spaced apart, when they are shot with a telephoto lens, it will look as though they are tightly clustered together.
By making use of compression effects you can take impressive photos, such as shots that emphasize the presence of your main subject, or purposely raise the information density within the angle of view.
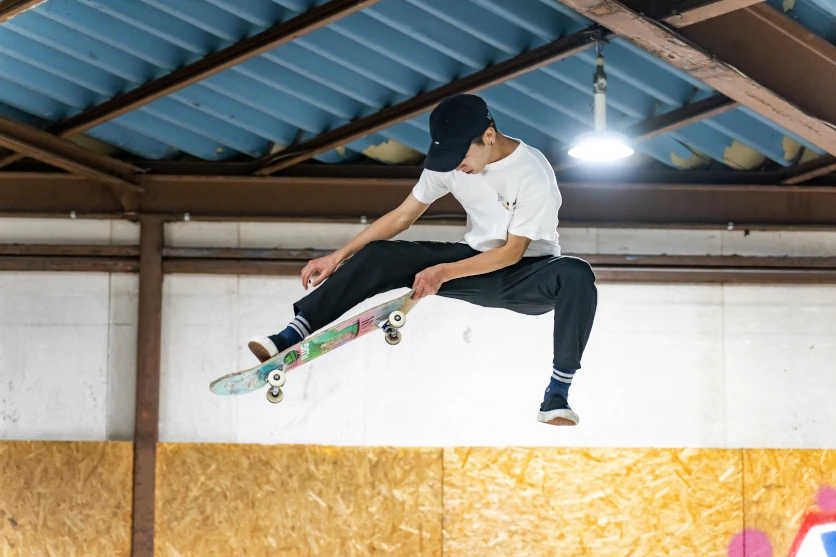
The third characteristic is the ease with which a telephoto lens allows you to produce background bokeh. In general, the longer the focal length of a lens, the shallower its depth of field (the range over which a subject is in focus), making everything apart from the section in focus produce bokeh. When you make use of this characteristic when shooting, you can get your main subject, such as a person, animal or plant life to stand out against the background.
While you can take photos that utilize background bokeh with a standard lens and other lenses, by combining it with compression effects and framing shots using the narrow angle of view, you can enjoy capturing images that showcase the unique qualities of telephoto lenses.
The fourth characteristic is how a telephoto lens allows you to crop in on a certain part of a scene. With its narrow angle of view, a telephoto lens allows you to take photos that focus on a limited part of a scene.
For example, even in a scene that features a mixture of potential subjects such as buildings, people or animals, you can capture only the subject you wish to main the main focus within the angle of view. This allows you to close in on fine details such as facial expressions or surface textures as if you are peering into the world from afar.
The angle of view of a lens changes depending on its focal length, and this also changes the mood of your photos. In general, telephoto lenses are broadly classified into three types:
・Medium telephoto (approx. 80-100mm)
・Telephoto (approx. 100-300mm)
・Ultra-telephoto (approx. 300mm or greater)
These types each have their own characteristics and a range of scenes for which they are best suited.
In this next section we will explore the characteristics of each type.
A medium telephoto lens is a lens with a focal length of around 80 - 100mm. This can be described as an angle of view that sits between a standard lens and a telephoto lens. A medium telephoto retains the characteristics of a telephoto lens while also combining some of the feel you get from a standard lens. This makes it easy to use when taking portraits and snaps that make use of bokeh and compression effects.
A telephoto lens is one with a focal length of around 100 - 300mm, and generally when we talk about telephoto lenses, we are referring to lenses whose focal lengths fall within this range. These lenses let you experience the angle of view and compression effects for which telephotos are known. With a telephoto lens you can properly capture distant subjects during sporting events, school sports days, when shooting animals, and so on.
An ultra-telephoto lens is one with a focal length of around 300mm or greater, and allows you to close in on distant subjects as well as enlarge small subjects. For example, an ultra-telephoto allows you to capture an enlarged view of an aircraft or other form of transportation, capture wild birds or other wildlife that is highly alert, or the detailed design elements of a large building. Ultra-telephoto lenses are also known for the strong compression effects they produce, which can help broaden the range of expression when shooting portraits and other shots.
A telephoto lens can produce unique expressions, not just by enlarging a distant subject, but through compression effects and bokeh. If you use a telephoto lens in skillful ways, you will be able to produce images that are distinct from those taken with wide-angle and standard lenses, even when working with the same subject. In this section we will introduce some scenes where the use of a telephoto lens is recommended, in order to give you a clear idea of when you can use a telephoto.
Telephoto lenses can be utilized in familiar situations such as sporting activities, various events, live concerts, and so on. For example, when you go to watch a sports match, you will be able to properly capture shows of the players from the venue’s spectator seating.
Children’s sports days are another case where a telephoto plays to its strengths. Many mothers and fathers want to keep clear images showing the expressions as scenes of their child doing their best while competing in a sports day. There are some cases where it is not possible to fully capture images of your child using a standard lens, but using a telephoto lens you can capture the subtly of their facial expressions or their entire body to full up the frame.
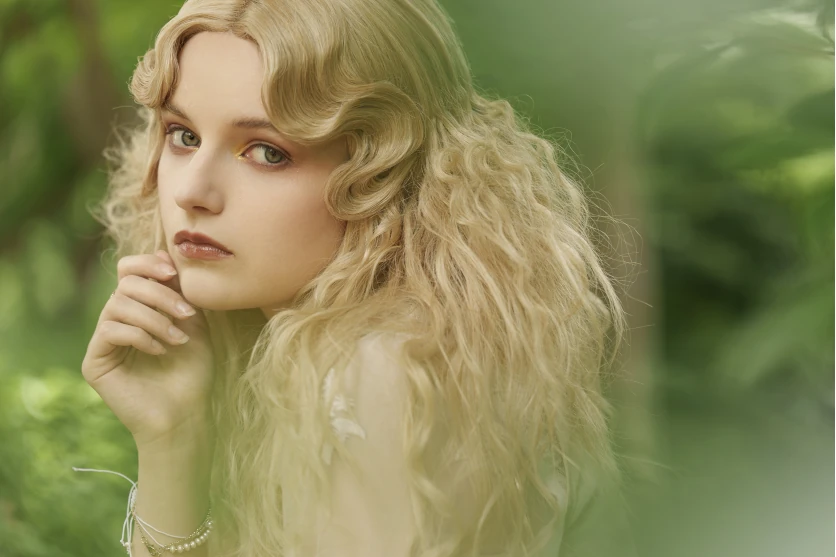
We also recommend using a telephoto lens for portraits. By closing in on the facial expressions of a subject layered over soft background bokeh, you can greatly enhance the impression and emotion in your subject. And by utilizing compression effects to bring in the background in an enlarged way, you can produce a three-dimensional effect and dynamic mood.
A telephoto lens is also great for shooting natural landscapes and cityscapes. You can close in on a particular building, tree or other party of a scene. In addition for scenes with densely packed buildings, people or plants, you can utilize the compression effects to further enhance the density and create powerful images.
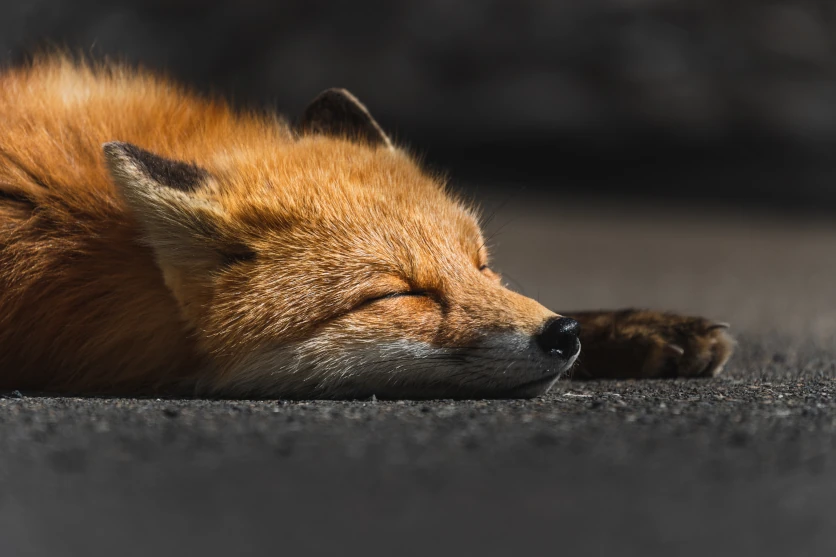
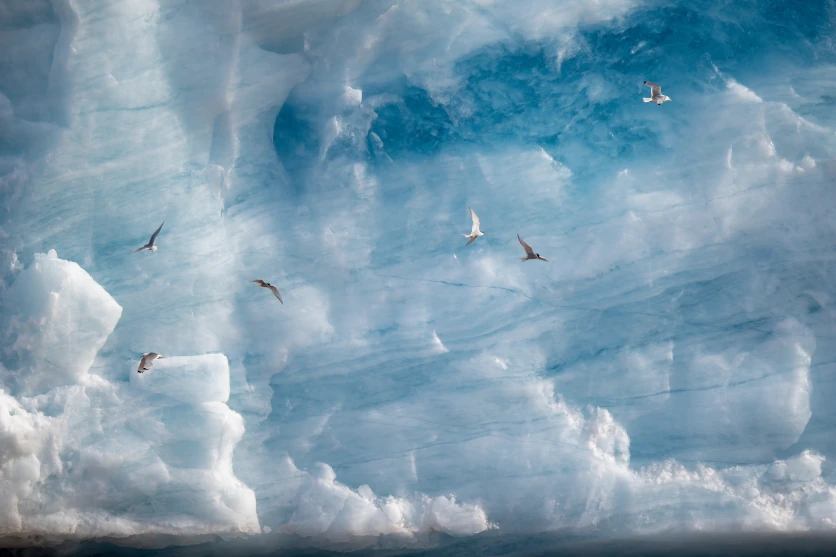
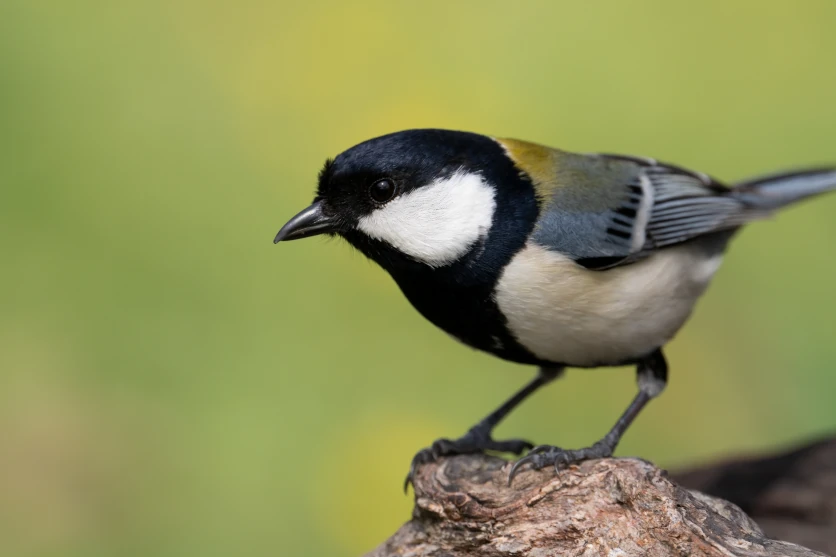
A telephoto lens really excels at capturing images of animals that you cannot get close to because they are highly alert. Typical examples are wild birds, shooting animals in a zoo, or photos of wildlife discovered while outdoors. With wild birds in particular, they may be small and quickly flee when approached. For these kinds of animals, using an ultra-telephoto lens can enable you to capture fine details in the subject even from a distance.
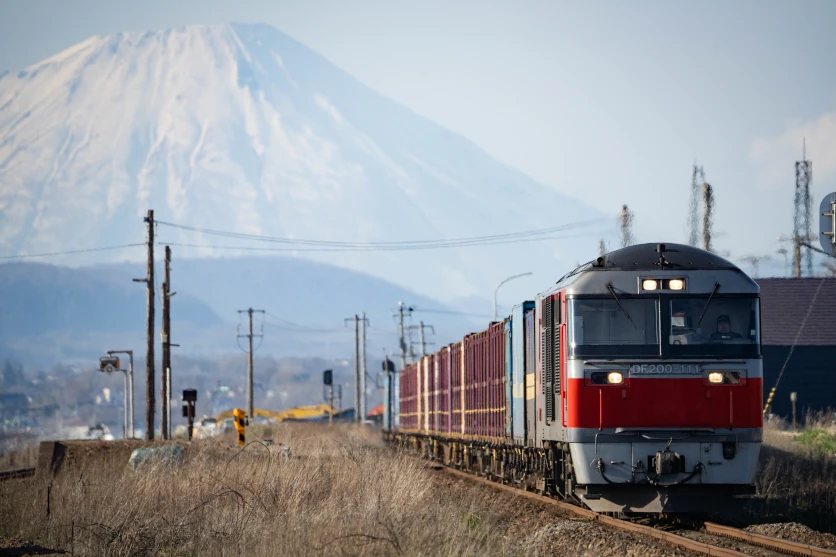
Telephoto lenses are often used to photograph trains, aircraft and other vehicles. We are not always free to get close to subjects such as aircraft and trains. That’s why we often need to photograph these subjects from a distance. That is where a telephoto lens comes in handy. Even when you cannot be physically close to a train or aircraft that appears far away, you can capture the fine details of the subject.
In addition to shots where you want to isolate a vehicle as the main subject, you should also experiment with framing that incorporates the background. By including nature or city scenes into the background, you can take advantage of compression effects to produce dynamic photos. In this way, a telephoto lens allows for a wide range of expressions depending on how you crop in on the subject in the image.
We recommend utilizing a tripod when shooting with a telephoto lens. As telephoto lenses can be large and heavy, one of the drawbacks is that they are susceptible to camera shake when shooting. Using a tripod can effectively suppress this camera shake. However, as you are sometimes in locations where the use of a tripod is restricted or cannot carry around a tripod, making full use of a vibration compensation mechanism can also suppress camera shake.
When shooting with a telephoto lens, shutter speed is one of the things you need to be mindful of. If your shutter speed is low, it is easier for camera shake to affect your image. That is why we recommend setting a higher shutter speed. A rule of thumb is to set the shutter speed to at least [1/focal length] to effectively suppress camera shake. If this results in inadequate exposure, try increasing the ISO sensitivity or utilizing exposure compensation. If possible, we also suggest using a tripod.
As noted above, one of the drawbacks of a telephoto lens is its susceptibility to camera shake. Try using your camera’s vibration compensation mechanism to suppress camera shake as much as possible. Depending on the model, your lens may also have a built-in vibration compensation mechanism, providing even more stable vibration compensation.
There is a wide lineup of telephoto lenses available. To avoid getting confused about what lens to choose, it is important to sort out what factors you are looking for in a lens and choose the lens that best suits the subjects you want to photograph and the environments in which you will be operating. In this section we will provide some advice on choosing the right telephoto lens.
The f-stop is a number indicating the amount of light that enters the lens. As the aperture is stopped down (narrowed), the f-stop number goes higher, and as the aperture is widened, the f-stop number falls. At a low f-stop value, a large amount of light enters the lens and there is a greater amount of bokeh, and in reverse, a large f-stop value reduces the amount of light, and also decreases the amount of bokeh. A state where the aperture of a lens is as large is possible is referred to as its maximum or wide-open aperture, and this also represents the lower limit of its f-stop value.
A lens with a large wide-open aperture (small f-stop value) is advantageous in that it allows you to take clear and bright photos even when a higher shutter speed is set in dark environments such as indoors or at night. Choose a lens with as large a wide-open aperture as possible will allow you to adapt to a variety of situations.
As noted above, telephoto lenses are broadly classified into three types depending on the focal length (medium telephoto, telephoto and ultra-telephoto). In general photography, a lens that covers from the medium telephoto to telephoto range is often enough, but an ultra-telephoto may be needed for certain subjects such as wild birds, wildlife or railway photography. Choose an appropriate focal length based on the images you want to capture.
How easy a lens is to carry around is another factor to take into account when choosing a telephoto lens. If your lens is as light and compact as possible, you will be able to carry it on long trips without it getting bulky. In addition, if the lens is lightweight it will put less strain on the body and help prevent camera shake. This can make it easier to take photos with high image quality even when you are restricted from using a tripod.
Whether a lens includes autofocus (AF) and vibration compensation mechanisms is another important point to check. Focus on whether the AF can focus on subjects speedily and accurately. When shooting wildlife or indoors, subtle operating noises can get in the way of shooting. That is why you should also check the operating noise made by the AF and how quiet the lens is.
As explained earlier, since vibration compensation is an important point for suppressing camera shake when using a telephoto lens, if the lens includes a build-in vibration compensation mechanism, you will be able to go about your photography with greater peace of mind.
Minimum object distance is the minimum distance at which the camera can bring objects into focus, and gives an indication of how close you can get to a subject and still photograph it. If you choose a lens with a short minimum object distance, you will be able to produce a wider range of expressions, such as by getting close into the subject and creating strong background bokeh.
A telephoto lens allows you to greatly enlarge a distant subject, and also features dynamic expressions from compression effects that the ability to produce beautiful bokeh. These lenses allow you to bring up unique charm in subjects across a wide range of shooting scenarios from sports to animals, vehicles and landscapes. Try to appreciate what makes telephoto lenses special and use them to take compelling images.

Lens Featured in this Impression
-

-
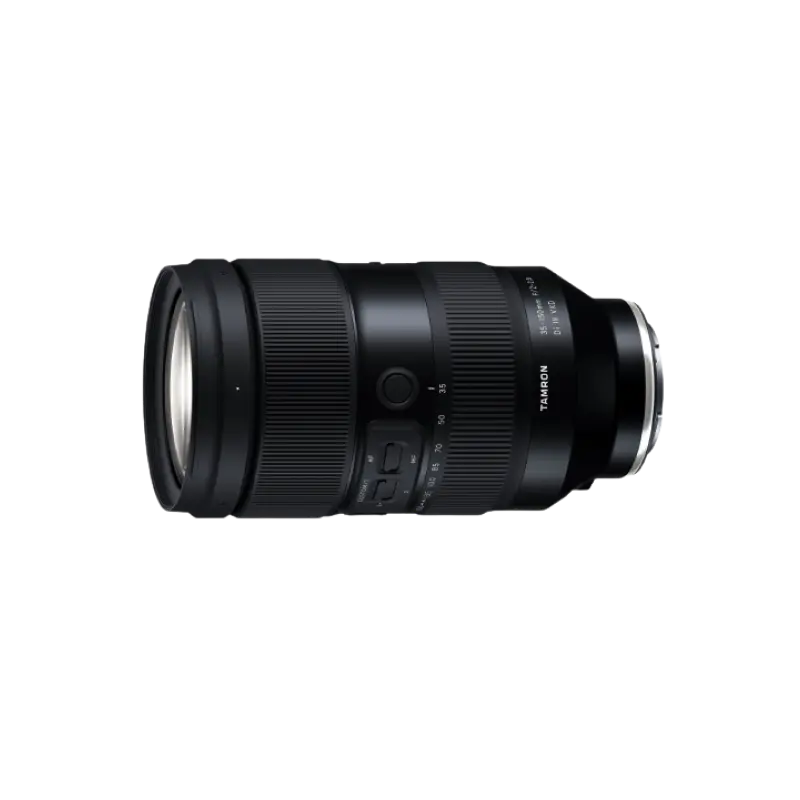
35-150mm F/2-2.8 Di III VXD a058(Model )
The 35-150mm F/2-2.8 Di III VXD (Model A058) is a high resolution travel zoom lens that covers everything from the 35mm wide angle to the 150mm telephoto focal length, the first zoom lens achieving an aperture of F2 at the wide angle end. It has a groundbreaking fast-aperture and utilizes the linear motor focus mechanism VXD (Voice-coil eXtreme-torque Drive), thereby achieving high speed, high precision autofocusing. The innovative lens design enabled us to greatly improve the lens's grip and functionality. The software, developed in-house, enables to easily customize functions and to update firmware.
-

-
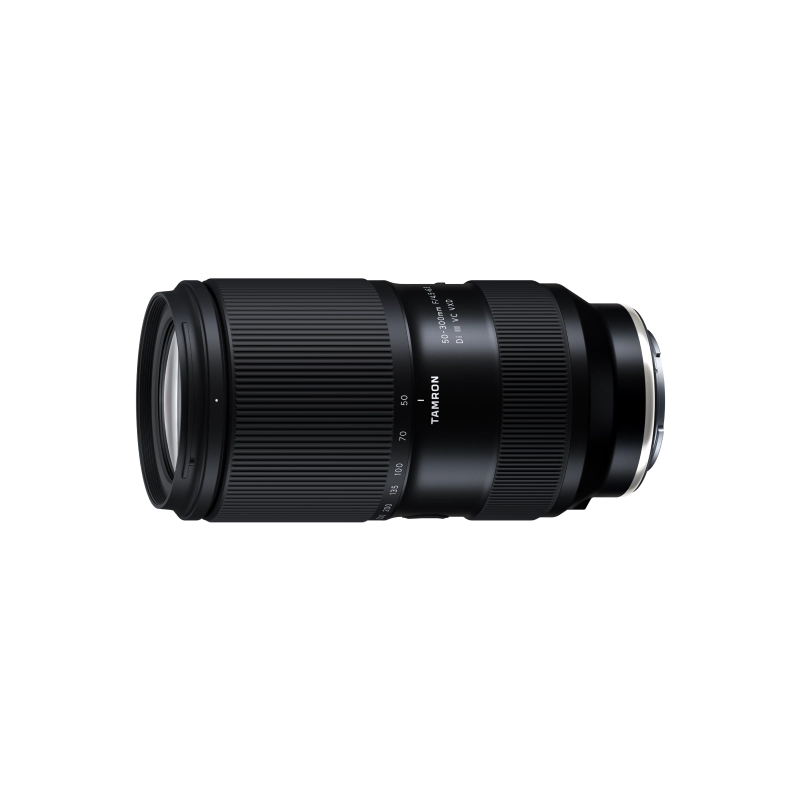
50-300mm F/4.5-6.3 Di III VC VXD a069(Model )
50-300mm F/4.5-6.3 Di III VC VXD (Model A069) is a 6x telephoto zoom lens for Sony E-mount that delivers outstanding convenience and image quality. Discover the groundbreaking capabilities of a 300mm telephoto zoom that starts from 50mm at the wide end.
-

-
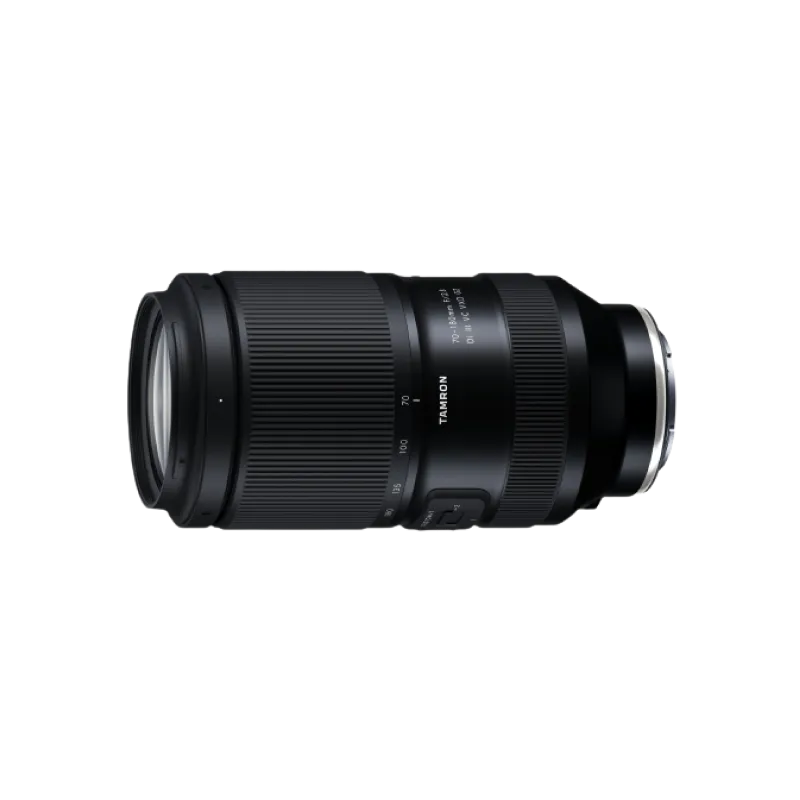
70-180mm F/2.8 Di III VC VXD G2 a065(Model )
70-180mm F/2.8 Di III VC VXD G2 (Model A065) has evolved to G2 level.This is the world’s smallest and lightest, fast-aperture telephoto zoom lens for Sony E-mount and Nikon Z mount with astounding portability and superb image quality.
-

-
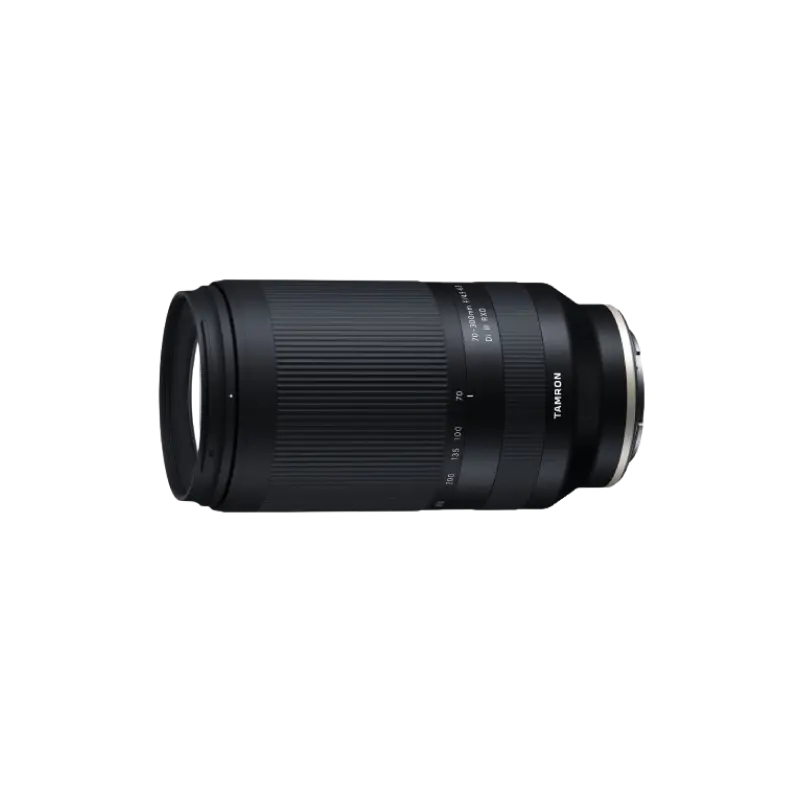
70-300mm F/4.5-6.3 Di III RXD a047(Model )
The 70-300mm F/4.5-6.3 Di III RXD (Model A047) for full-frame mirrorless cameras is a telephoto zoom lens designed and created so photographers of all skill levels can enjoy high quality images comfortably. The 70-300mm F4.5-6.3 covers a broad telephoto zoom range yet is the small and lightest weight. With special emphasis on resolving power, TAMRON has deployed special lens elements appropriately arranged to correct chromatic aberration, generally very strong in a telephoto lens, as well as other aberrations. Users can enjoy high-resolution images combined with stunning bokeh qualities that are achievable only with a telephoto lens. The lens also incorporates the RXD, a high-speed precision AF drive system that is remarkably quiet. The 70-300mm F4.5-6.3 is a versatile lens for photographing landscapes, sports and other action, pets, wildlife, and more. The lens also demonstrates its potential for portrait shooting, casual snapshots, and scenarios that require you to be mobile and shoot handheld, like sporting events.
-

-
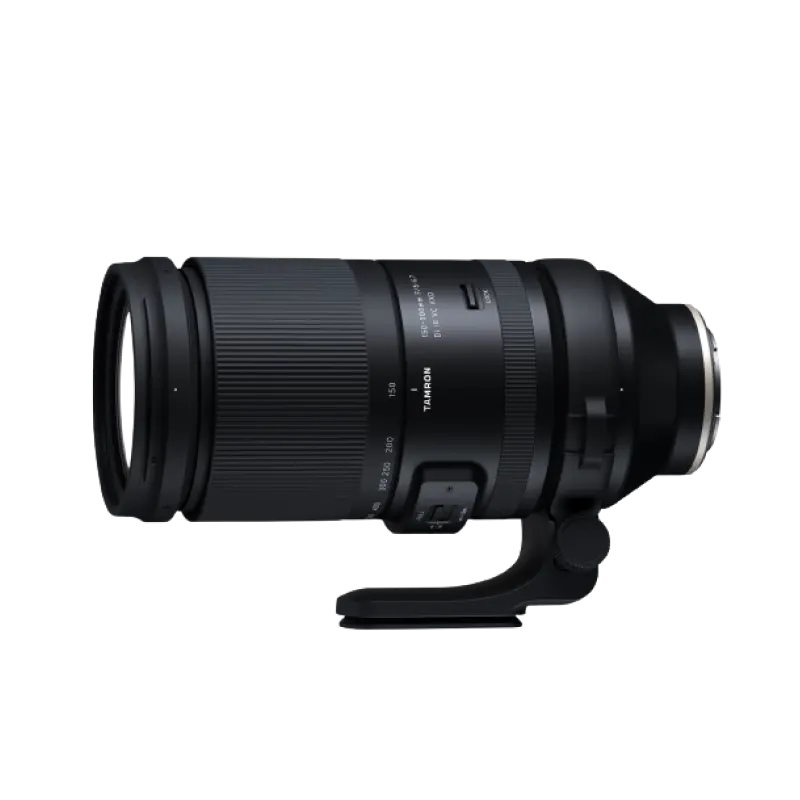
150-500mm F/5-6.7 Di III VC VXD a057(Model )
The 150-500mm F/5-6.7 Di III VC VXD (Model A057) is compact enough to be handheld while maintaining a focal length of 500mm on the telephoto end. It allows users to easily enjoy the world of the 500mm ultra-telephoto lens while maintaining its high image quality. The high-speed, high-precision AF with excellent tracking performance and the VC mechanism support handheld shooting in the ultra-telephoto range.