Initiatives to Become a Resource Recycling Society
Toward the realization of a resource recycling society
In order to create a sustainable society without depleting limited resources, we need to create a circulation-based society in which we produce with few resources and energy , reduce waste, and reuse resources. It is possible.
TAMRON works on 3R which are reduction of raw materials and waste (Reduce), to reuse materials and water can be used repeatedly(Reuse), and recycling waste as material (Recycle), for circulating resources efficiently.
Material Balance
In Japan, TAMRON carries out design work, creates prototypes, fabricates metal molds and molds plastic components at its head office plant located in Saitama Prefecture, while the Aomori Factory (Namioka Site) manufactures lenses and the Aomori Factory (Hirosaki Site) assembles products. TAMRON manufactures parts and assembles products at TAMRON Optical (Foshan) in China and at TAMRON Optical (Vietnam).
These sites use electricity, heavy oil, kerosene and other energy sources for developing, designing and manufacturing, which produce CO2. Our plants in Namioka, Foshan and Vietnam also use water for polishing and cleaning lens elements. The head office and TAMRON Optical (Foshan) manufacture plastics used to make peripheral components for lenses, and these processes produce runner materials(*1) and other waste. Air cargo, marine shipping, and trucks are used to transport components and products between plants, which results in CO2 emissions from the burning of fuel.
*1 Waste material that occurs when pouring plastic resin during the production process.
| INPUT | TAMRON | OUTPUT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Unit | |||||||
| Iron | 8,174 | t |
Procurement of raw materials and parts |
CO2 emissions | 240,389 | t-CO2 | ||
| Glass | 33,137 | t | ||||||
| Plastic | 5,735 | t | ||||||
| Resin | 2,569 | t | ||||||
| Paper | 515 | t | ||||||
| Chemicals | 741 | t | ||||||
| Cardboard | 898 | t | ||||||
| Energy | 799,000 | GJ |
Development, design and production at TAMRON |
CO2 emissions | 38,871 | t-CO2 | ||
| Electric power | 87,847 | 103 kWh |
Electric power | 38,358 | t-CO2 | |||
| Heavy oil | 121 | kℓ | Heavy oil | 328 | t-CO2 | |||
| Kerosene | 2 | kℓ | Kerosene | 5 | t-CO2 | |||
| Diesel | 8 | kℓ | Diesel | 21 | t-CO2 | |||
| Gasoline | 1 | kℓ | Gasoline | 2 | t-CO2 | |||
| LPG | 4 | 103㎥ | LPG | 22 | t-CO2 | |||
| Natural gas | 60 | 103㎥ | Natural gas | 134 | t-CO2 | |||
| Dry ice | 1 | t | Dry ice | 1 | t-CO2 | |||
| Water | 747 | 103㎥ | Water discharged | 458 | 103㎥ | |||
| Clean water | 596 | 103㎥ | Products | 1,101 | t | |||
| Groundwater | 150 | 103㎥ | ||||||
| Rainwater | 1 | 103㎥ | ||||||
| Water reused and recycled | 24 | 103㎥ | Total amount of discharged matter generated | 2,366 | t | |||
| Chemicals | 8 | t | Industrial waste (*2) | 1,868 | t | |||
| General waste | 498 | t | ||||||
| Recycling | 1,359 | t | ||||||
| Plastic (*3) | 531 | t | ||||||
| Cardboard | 244 | t | ||||||
| Genaral waste (thermal recycling) |
97 | t | ||||||
| Waste liquid | 196 | t | ||||||
| Waste oil | 50 | t | ||||||
| Metal | 168 | t | ||||||
| Paper | 23 | t | ||||||
| Polishing sludge | 12 | t | ||||||
| Other | 38 | t | ||||||
| Energy (*1) | 154 | kℓ |
Transportation |
CO2 emissions | 394 | CO2 | ||
| Diesel | 128 | kℓ | Diesel | 334 | t-CO2 | |||
| Gasoline | 26 | kℓ | Gasoline | 60 | t-CO2 | |||
| Electric power | 2,967 | 103kWh |
Use |
CO2 emissions | 202 | t-CO2 | ||
Sites covered : Head office (including Sales Office), the plants in Aomori Prefecture, TAMRON Optical (Foshan) and TAMRON Optical (Vietnam).
Site coverage : 96%
Reference guideline : Manual for Calculating and Reporting Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ver. 6.0
*1 Data during transportation covers energy used to transport parts and finished products by ground and commercial vehicles connecting TAMRON’s satellite offices in Japan and TAMRON Optical (Vietnam). TAMRON Optica(l Foshan)data covers company-owned vehicles only.
*2 Regarding to Pollutant Released & Transfer Registered(PRTR)substances, industrial waste includes 1.3 tons of xylene and 1.2 tons of ethylbenzene. 2.3 tons of xylene, 2.1 tons of ethylbenzene, and 0.0029 tons of Methylnaphthalene were also released into the atmosphere.
*3 The amount of plastics recycled represented 94 tons of thermal energy and 436 tons of material.
4 In response to the Act on Rational Use and Proper Management of Fluorocarbons, we are striving to grasp the amount of refills and recovery by carrying out simple inspections and regular inspections at target sites that manage Class 1 specified products in accordance with theAct. The amount of fluorocarbon leakage in fiscal 2024 was less than 1,000 tons per year, below the level at which reporting to the government becomes mandatory.
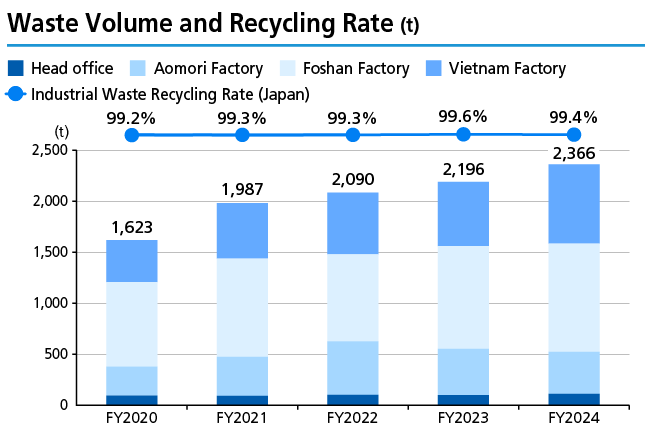
Waste Reduction
Waste volume increased 7.7% year on year in 2024, and the industrial waste recycling rate in Japan was 99.4%. Waste volume decreased 5% in Japan and increased 12% at overseas plants. The increase in waste volume outside Japan is mainly due to a rise in sludge generated by increased production at TAMRON Optical (Vietnam).
Promoting Design for the Environment (DfE)
TAMRON manufactures environmentally friendly products by placing emphasis on the 3 Rs (reduce, reuse and recycle). At the design review stage of product development, we assess the extent to which we have achieved a longer service life (longer use, easier repair), resource savings (lighter weight, more compact, reduction in the number of parts, use of recycled materials, easier disassembly), and energy savings (lower power consumption at manufacture and use stages). Products that are environmentally friendly and that meet TAMRON voluntary standards are certified as being TAMRON Eco Label products. See here for certified products.
Regulation of Hazardous Substances
TAMRON has formulated regulations for the management of environment-related substances to comply with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, the Regulation concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) and other laws and regulations restricting chemicals contained in products. Accordingly, we have constructed a environmental and quality assurance system for ensuring the management of hazardous substances and the prevention of contamination.
The regulations for the management of environment-related substances are designed to comply with relevant laws and regulations, satisfy customer requirements, preserve the global environment and minimize the impact on ecosystems. Accordingly, we have set control levels for each hazardous chemical substance, and in addition to prohibiting the use of some chemical substances in components and materials, we have designated some substances whose use will be prohibited upon reaching a specified deadline. TAMRON is continuing with efforts to discontinue the use of hazardous chemical substances in a systematic and stepwise manner towards these specified deadlines.
The cooperation of suppliers is an essential part of building this environmental quality assurance framework. TAMRON only begins doing business with suppliers of components and raw materials once it has verified that they have appropriately established environmental management systems and chemical substances management systems. In addition, even after business dealings have begun, TAMRON provides suppliers with Regulations for the Management of Environment-related Substances which detail hazardous chemical substances whose use is prohibited, Guidance on Environmental Quality Assurance Systems which explains procedures for preventing hazardous chemical substance contamination, and Environmental Quality Management Procedures, while also asking suppliers to cooperate with audits and other activities.
In consideration of the possibility of hazardous chemical contamination, we possess an array of measuring instruments including an X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzer, an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) analyzer, and a gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyzer to examine whether there is any lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, brominated flame retardants (PBB and PBDE) or four phthalic esters (DEHP, BBP, DBP and DIBP) contained in components/ raw materials, or products and to quantify the amounts when detected.
(*1) Polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) are mainly used as flame retardants in plastics, rubber and tapes. These substances are registered as endocrine disruptors (environmental hormones), and are suspected of causing central nervous system issues such as memory loss and depression, as well as retarded growth in children, liver disorders and enlarged thyroids.
Cooperation with outside organizations to realize a resource recycling society
Creating a resource recycling society that limits the waste generated from business activities and reuses output as resources rather than waste is not something TAMRON can accomplish on its own. For this reason, TAMRON cooperates with its partners regarding the waste generated in connection with its business activities, promoting the reuse of used electronic equipment, and the recycling of metal, paper and various other materials. Recycling partners are selected based on criteria designated by TAMRON, and TAMRON representatives also conduct regular on-site audits of existing partners to verify that processing is being conducted appropriately.
Realization of plastic recycling
For TAMRON, the effective use of waste plastic runner materials (*1) is a key issue. To reduce the amount of waste output from our production processes, we manufacture the rear caps for our DSLR camera lenses from 100% recycled plastic runner materials. Between FY2010 and FY2024, we used a total of 216.5 tons of recycled materials (producing 9.88 million rear caps).
TAMRON has also considered new recycling methods at Integrated Design, Production Technology and Production Sub-committee meetings to further promote recycling. As a means of reducing waste while maintaining quality standards and ensuring that product functionality is not affected, TAMRON adopted "Preconsumer Closed Recycling, which involves mixing recycled materials with virgin materials. Since FY2017, TAMRON started to utilize these recycled materials for the mass production of the filter screw rings, a component of interchangeable lens for SLR cameras. TAMRON will continue to expand the introduction of recycled materials in components, examine new areas to target and promote waste reducing and recycling.
*1 Waste material that occurs when pouring plastic resin during the production process.

<Flow of recycling>
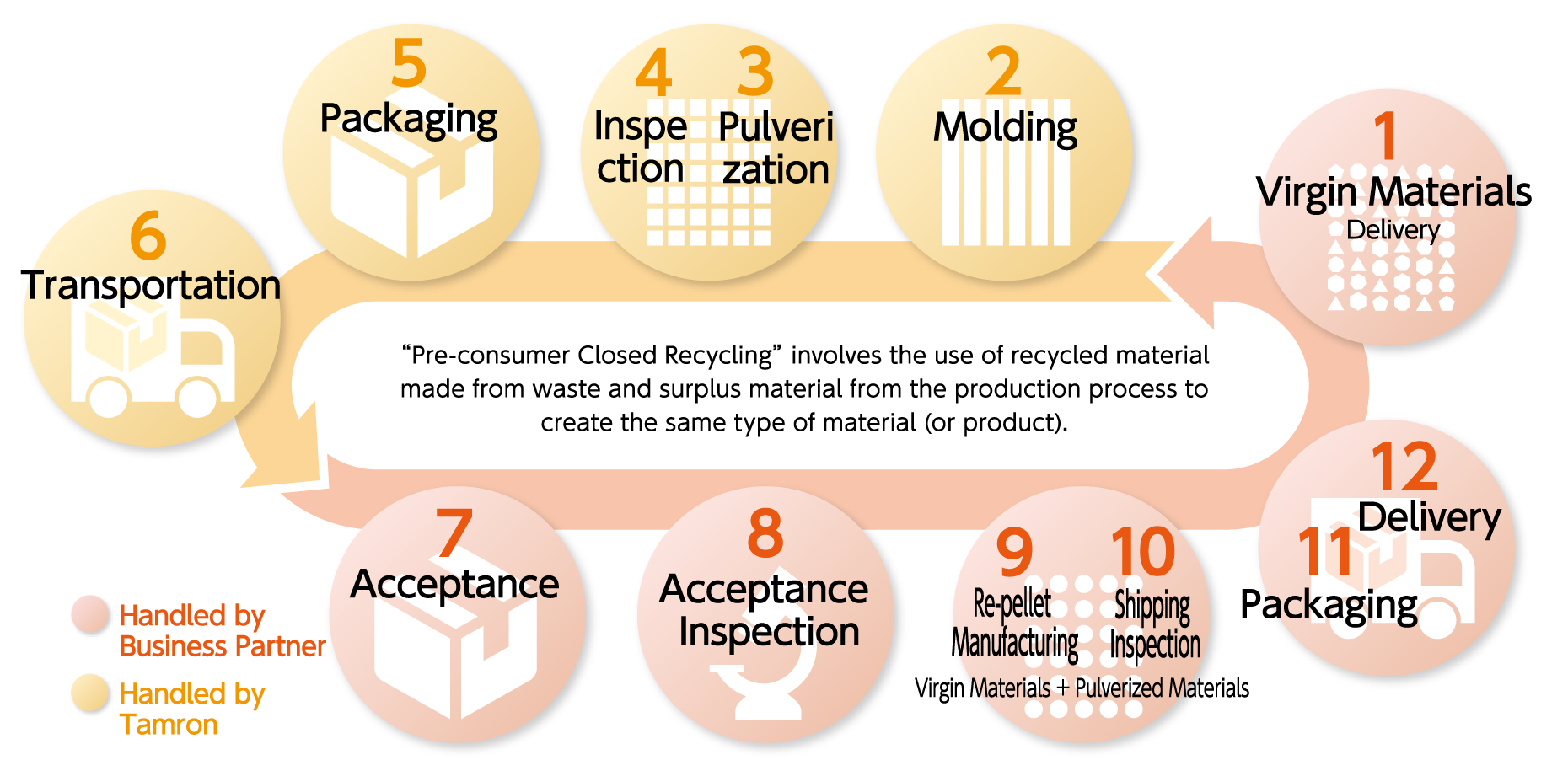
Recycling of TAMRON products
Products manufactured by TAMRON are sold around the world. TAMRON has launched an initiative to recover products that have finished serving their role of delivering excitement and peace of mind in the hands of customers, so that they can be reused or recycled. Collected TAMRON products, particularly interchangeable camera lenses, become resources in a recycling society that aims to limit resource inputs and consumption while maximizing resource value, minimizing resource consumption and curbing waste generation.
Particularly in Europe, the collection and recycling of used electronic and electrical devices in each country is legally mandated by the WEEE Directive. At TAMRON, our German sales subsidiary is registered with used electronic and electrical equipment collection organizations in Germany and Austria, while official sales distributors of TAMRON products in each country are registered with similar organizations, thereby cooperating with the collection and recycling of TAMRON products. More specifically, in Germany, TAMRON's German sales subsidiary takes part in a used electronic and electrical device collection organization that maintains around 100 collection points. When individuals with used electronic and electrical devices including TAMRON interchangeable camera lenses bring them to these collection points, they are collected free of charge. The used electronic and electrical devices that have been collected are processed for recycling, including shredding and the separation of metals. The collection organization in which TAMRON's German sales subsidiary takes part pursues two goals: to reduce the amount of waste, and to conserve natural resources by reusing valuable secondary raw materials contained in electronic products.
* Official sales distributors of TAMRON products are located in a total of 22 countries, including Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic and Denmark.
